
When customers ask for plastics that can survive high heat, there are several datasheet properties that provide a useful starting point. We covered these fundamentals in our guide to two properties that define high-temperature plastics, and they can help frame the discussion around ultra-high-performance materials like polyimides (PI).
Key Temperature Terms
Continuous Use Temperature (CUT)
The highest temperature a material can endure over time without losing half its strength.
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT)
The temperature at which a material softens under load as measured by ASTM D648.
Melting Temperature (Tm)
The point at which semicrystalline polymers melt.
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
The temperature at which amorphous polymers soften.
Navigating High-Temperature Choices
As temperature rises, the set of polymers you can use shrinks. The best high-performance materials maintain strength and stiffness while resisting oxidative degradation. The chart below shows stiffness retention reference values for six Mitsubishi Chemical Group (MCG) high-temperature materials measured using Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA). While all offer elevated thermal capabilities, the Duratron™ PI grades stand out as temperatures approach and exceed 500°F (260°C).
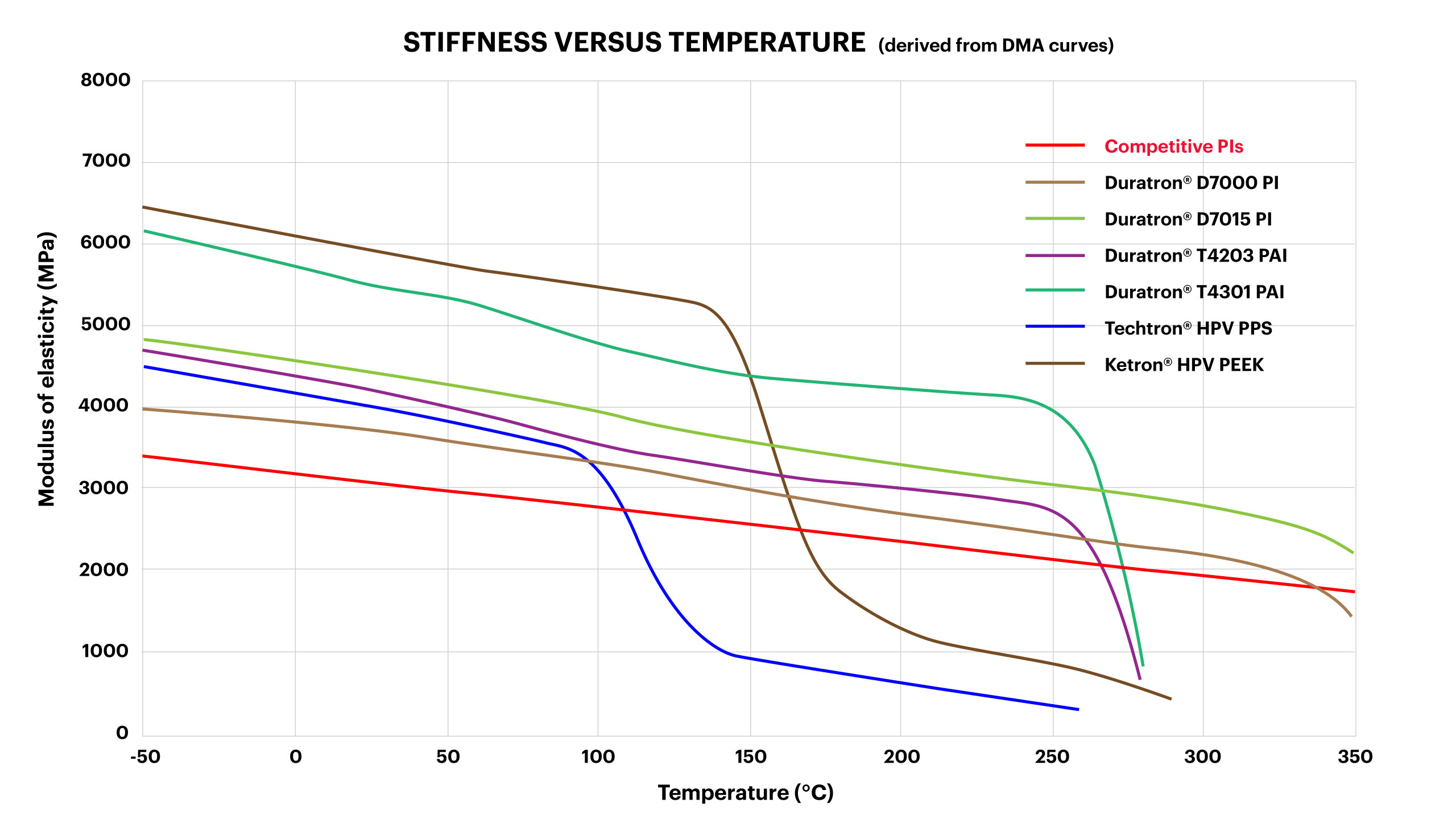
At room temperature, Ketron™ polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and Duratron™ polyamide-imide (PAI) grades begin with similar stiffness. As temperature rises, Ketron™ PEEK softens sharply around 300°F (150°C)—its glass transition temperature—making it less suitable for sustained high-heat applications. Duratron™ PAI maintains higher stiffness across a wider temperature window, but begins to decline as temperatures approach 480°F (~250°C). Techtron™ polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), while useful in elevated-heat environments, shows an earlier decline in stiffness relative to the others.
In contrast, Duratron™ PI grades retain stiffness further into extreme temperature territory, demonstrating why PI are often chosen for continuous service beyond the upper limits of melt-processable materials like PAI and PEEK.
This temperature-dependent performance profile highlights the sweet spot for Duratron™ PI: applications operating above 480°F (~250°C) where long-term strength and dimensional stability are critical.
Quick Reference Guide
The table below provides a thermal performance snapshot, highlighting the temperature at which each material excels.
| Measurement |
Duratron™ CU60 PBI |
Duratron™ D7000 PI |
Duratron™ T4203 PAI |
Ketron™ 1000 PEEK |
| HDT (°F) | 800 | 671 | 532 | 320 |
| CUT (°F) | 590 | 570 | 500 | 480 |
| Tm (°F) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 644 |
| Tg (°F) | 775 | 705 | 527 | N/A |
Need support with a high-temperature application?
We’re here to help you serve your customers with confidence.
Share application details and our team will recommend the most effective MCG grade and shape.
Contact us to get started.

Simplify Your Workflow with MCAM Connect
Easily manage orders, access critical data, and get tailored support — all from one powerful platform.